Hello! It’s me again! I wrote some Python programs on Linear Algebra, and I’ll be introducing you to them in this guide. But first I have to tell you what linear algebra is.
Linear algebra is basically plotting a line on a graph. I don’t really know what the results in Google says, so I think this is the shortest explanation. But I digress.
Contents
Equation of a Straight Line
This is the equation of a straight line-
![]()
![]() is the gradient, or the slope of the line. The higher the value of
is the gradient, or the slope of the line. The higher the value of ![]() , the steeper the line is.
, the steeper the line is.
![]() is the y-intercept of the line. It is where the line crosses the y-axis.
is the y-intercept of the line. It is where the line crosses the y-axis.
And ![]() and
and ![]() are the coordinates of a point the line passes through.
are the coordinates of a point the line passes through.
Here is an example:
![]()
In this straight line equation, 2 is the gradient and 1 is the y-intercept. Before we plot the line, we have to start marking some points first! We start substituting ![]() by one value, and then increasing it by 1.
by one value, and then increasing it by 1.
Example
In this case, I want ![]() to start with -2. We can solve for
to start with -2. We can solve for ![]() then!
then!
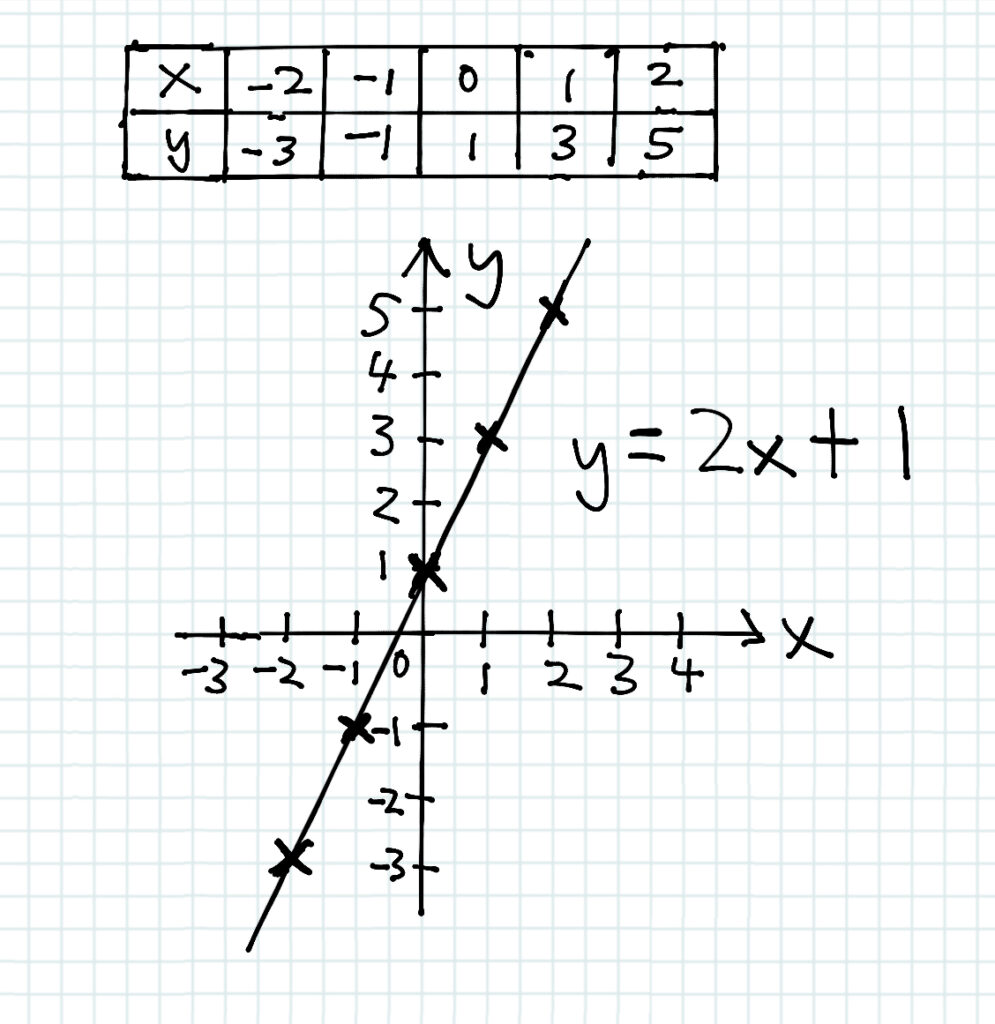
Calculating the Gradient
So, we already know that ![]() means the gradient. But how do we calculate it?
means the gradient. But how do we calculate it?
Let’s say Point A’s coordinates are (![]() ,
,![]() ) and Point B’s coordinates are (
) and Point B’s coordinates are (![]() ,
,![]() ). We can use this formula to calculate the slope-
). We can use this formula to calculate the slope-
![]()
For example, Point A’s coordinates are (-2, 1). Point B’s coordinates are (2, 9).
Then we substitute it in the formula and solve for the gradient-
![]()
![]()
![]()
So the gradient here is 2.
Positive and Negative Gradients
There are also positive and negative gradients. Lines with a positive gradient go up from left to right, and lines with a negative gradient go down from left to right.
You can see if the line has a positive or negative gradient by imagining yourself starting from the left and walking up the line. If you can walk up, it’s positive, and if you can’t it’s negative.
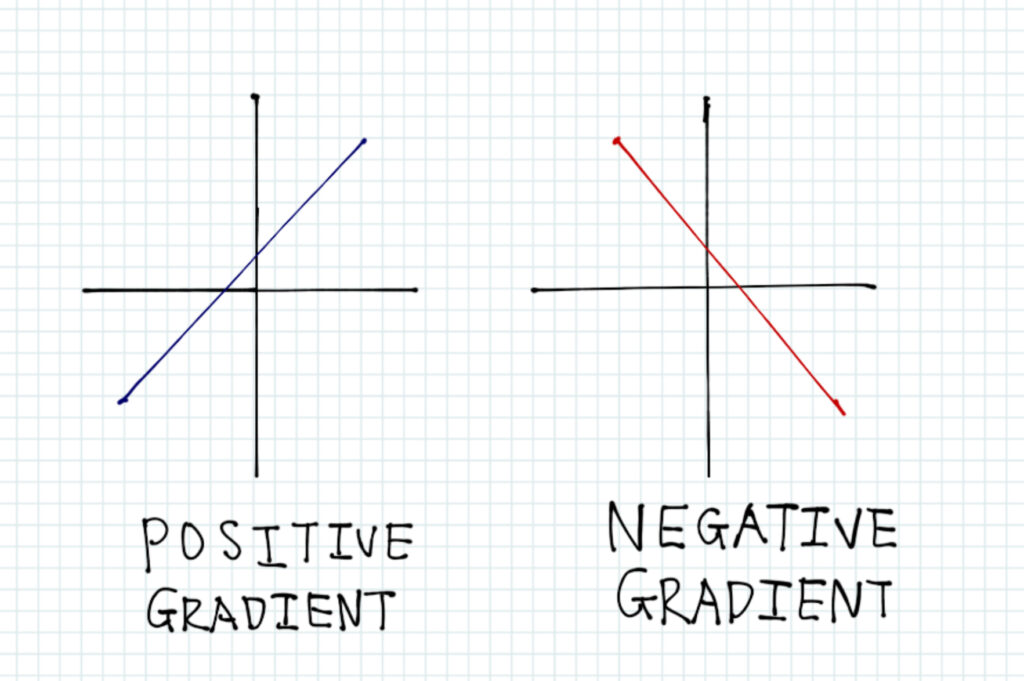
This equation has a positive gradient, so this line goes upwards-
![]()
And this equation has a negative gradient, so this line goes downwards-
![]()
Then there are these types of lines I call the special cases. They are the horizontal line and the vertical line.
The horizontal line looks like this, and doesn’t have a gradient.
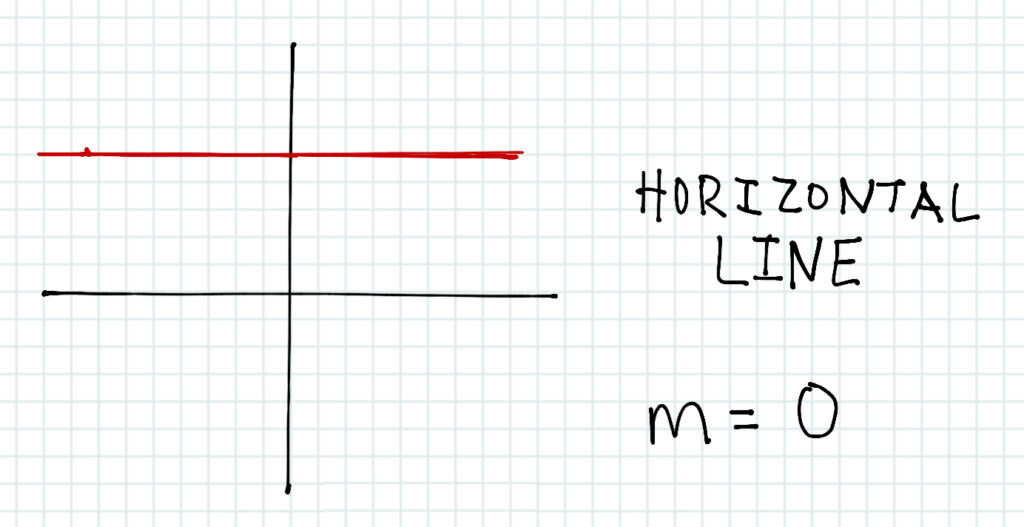
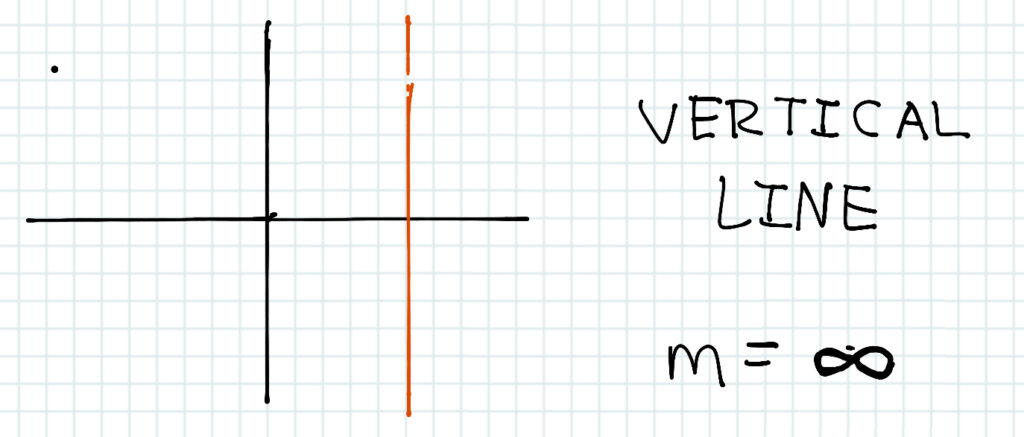
The vertical line looks like this, but the gradient is infinity, since it goes straight up.
Intercepts
The x-intercept is the point at which the graph crosses the x-axis. The y-coordinate is zero at this point.
The y-intercept is the point at which the graph crosses the y-axis. The x-coordinate is zero at this point.
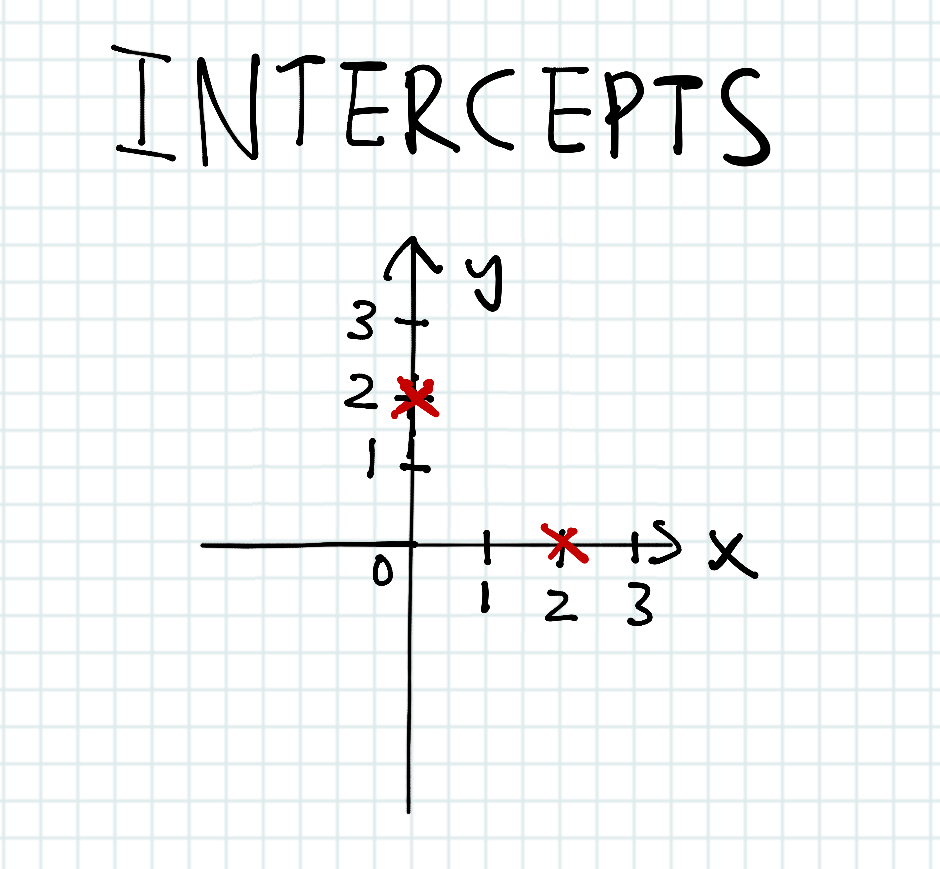
In this picture, the intercepts are pretty clear. The x-intercept is on point (2,0) and the y-intercept is on point (0,2).
Conclusion
So, that’s the basics of the basics of linear algebra. Yes it’s only the basics, of the basics.
However, I did say that I wrote some Python programs to help you out on this topic. I’ll introduce you to one of them on the next page. But you should take a break. You deserve it after reading THIS WHOLE PAGE!!
Next, I’ll show you how to find the straight line equation given two points. Click here!
